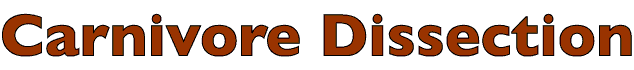
LAB 6 Introduction
Pelvic Limb Muscles:
Caudal Hip, Cranial Thigh, and Cranial Crus
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 62-67)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Observe the four muscles comprising the caudal hip group:
- gemelli
- internal obturator
- quadratus femoris
- external obturator
• Regarding cranial muscles of the thigh, find . . .
- quadriceps femoris m., which has four heads:
-- rectus femoris
-- vastus lateralis
-- vastus intermedius
-- vastus medialis
- iliopsoas m. insertion on the femur
(also, observe the articularis coxae m., a surgical landmark)
• Identify three major muscles within craniolateral muscles of the crus:
- cranial tibial m.
- long digital extensor m.
- peroneus longus m. (fibularis longus m.)
(peroneus brevis m. & lateral digital extensor m. need not be dissected)
•Identify crural deep fascia and the two components of extensor retinaculum (crural & tarsal extensor retinaculum)
Anatomical Terms:
Pelvic Limb: muscles & fascia (continued)
Hip (caudal muscles)
internal obturator m.
gemelli mm.
quadratus femoris m.
external obturator m.
Thigh (cranial muscles)
quadriceps femoris m.:
rectus femoris m.
vastus lateralis m.
vastus intermedius m.
vastus medialis m.
(patella & patellar ligament)
iliopsoas m.
psoas major m.
iliacus m.
Leg (Crus)
superficial crural fascia
deep crural fascia
crural extensor retinaculum
tarsal extensor retinaculum
Leg (Crus) (craniolateral muscles)
cranial tibial m.
long digital extensor m.
fibularis (peroneus) longus m.
lateral digital extensor m.
fibularis (peroneus) brevis m.
Note:
The "p" is silent in the term "psoas" [psoa = Greek, loin muscle].
Peroneus and fibularis are synonyms [perone = Greek, fibula].
The terms "sciatic" [L.] and "ischiatic" [G.] are synonyms for ischium.
Instructor Commentary:
The caudal hip muscles (internal & external obturator, quadratus femoris, and gemelli) rotate the femur so the stifle turns outward (supination-like effect). Thus they antagonize the tendency of the middle gluteal muscle to pronate the femur (stifle inward).
In contrast to the thoracic limb, the pelvic limb has few extrinsic limb muscles (running from the trunk to limb bones). The major extrinsic muscle is the psoas major, which joins the iliacus m. to form the iliopsoas m. Other "extrinsic" limb muscles are either small (superficial gluteal m.) or they attach to the os coxae which is immobile (psoas minor m. & coccygeus, m.)
The cat lacks the sacrotuberous ligament encountered in this lab. Because of the absence of a sacrotuberous ligament, proximal muscle fibers of the biceps femoris m. become a separate caudofemoralis m. in the cat (in the dog the proximal muscle fibers attach to the sacrotuberous ligament and remain with the biceps femoris m.).
You might regard the patella as a sesamoid bone within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris m., rather than calling the connection between the patella and tibia a "patella ligament". However, because patella ligaments are multiple and elaborate in other species, the concept of a ligament rather than a tendon is used.
In preparation for this lab, study prominent features of the tibia & fibula and tarsal bones (metatarsal bones and phalanges of the pes are similar to comparable bones of the manus).
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
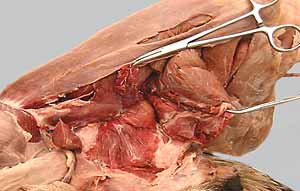
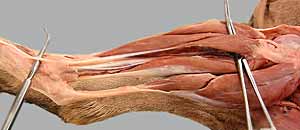
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 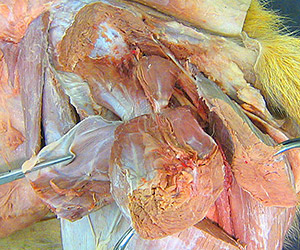 |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 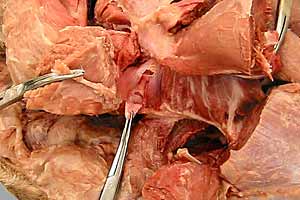 |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 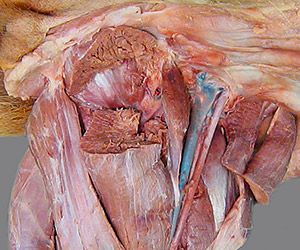 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 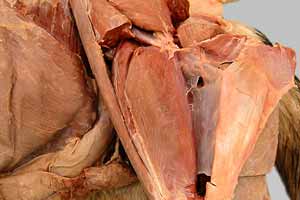 |
 |
8 |
| 9 |  |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 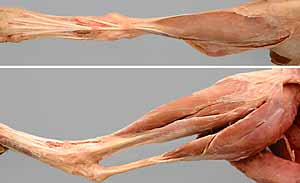 |
 |
12 |
| 13 | 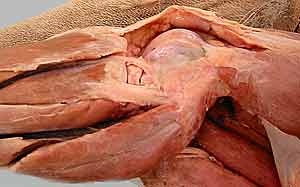 |
 |
14 |
| 15 | 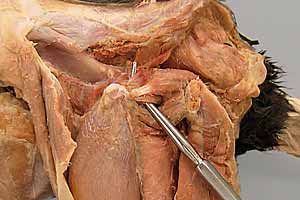 |
 |
16 |