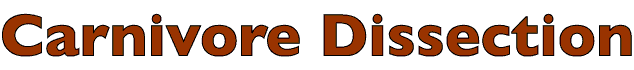
LAB 9 Introduction
Epaxial Muscles &
Neck Vessels and Nerves
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 90-94 & 96-98)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Remove thoracolumbar deep fascia to expose underlying epaxial muscles.
• Examine the organization of epaxial muscles (three longitudinal systems,
each system subdivided transversely per region):
- iliocostalis system (lumborum & thoracis regions)
- longissimus system (lumborum, thoracis, cervicis, & capitis)
- transversospinalis system (named muscles, especially
large in the neck)
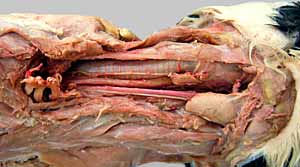
•Identify "two" transversospinalis epaxial muscles in the neck
- splenius m.
- semispinalis capitis m. (two parts: biventer cervicis m. & complexus m.)
• In the dog, examine the elastic nuchal ligament, which is a continuation of the collagenous
supraspinous ligament.
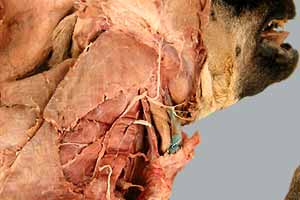
•Reflect skin from the neck and thorax on the right side. Find the following cervical nerves:
- great auricular n. (and transverse cervical n.)
- accessory n.
- vagosympathetic nerve trunk
Anatomical Terms:
Trunk and Neck: epaxial muscles, etc.
Iliocostalis System
iliocostalis lumborum mm.
iliocostalis thoracis mm.
Longissimus System
longissimus thoracis et lumborum
longissimus cervicis
longissimus capitis
Transversospinalis System
splenius m.
semispinalis capitis m.
biventer cervicis m.
complexus m.
supraspinous ligament (absent in cat)
nuchal ligament (absent in cat)
Neck: nerves & vessels
second cervical nerve (ventral branch)
great auricular nerve
transverse cervical nerve
external jugular vein [palpate]
mandibular lymph nodes [palpate]
medial retropharyngeal lymph node
superficial cervical lymph nodes [palpate]
accessory (eleventh) cranial nerve
ventral branches of cervical nerves 3,4,5
vagosympathetic nerve trunk
Note:
nucha [Latin] = nape of the neck (nuchal ligament)
longissimus [Latin] = longest (longissimus system)
epi- or ep- [Greek.] = on/upon/over (epaxial muscles)
supra- [Latin] = above (supraspinous ligament)
auricularis [Latin] = pertaining to the ear (great auricular n.)
auris [Latin] = ear
et [Latin] = and (thoracis et lumborum)
Instructor Commentary:
Epaxial muscles (epi = upon & axial = axis) are muscles located dorsally along the spine. They are innervated by dorsal branches of spinal nerves and function to extend the vertebral column. Generally, epaxial musculature consists of fascicles running from one vertebra to neighboring vertebrae. As defined in your Dissection Guide (Fig. 2-81), we will divide epaxial musculature into three longitudinal systems (lateral, intermediate and medial) and further subdivide each system transversely by region. In the neck, the mass of epaxial musculature is greatly increased and we will identify individual muscles there.
The cat lacks nuchal and supraspinous ligaments, perhaps this contributes to its greater flexibility compared to the dog. As you will see, the elastic nuchal ligament is best developed in grazing ungulates who have more need for a passive head-elevation aid.
Spinal nerves innervate muscles and skin via dorsal and ventral regional branches. The dorsal branch gives rise to a dorsal cutaneous nerve and it innervates epaxial mm. The ventral branch gives rise to ventral and/or lateral cutaneous nerves and innervates hypaxial mm.
There are eight bilateral pairs of cervical spinal nerves. The first cervical nerve is small and it does not contribute to cutaneous innervation. Thus, the great auricular n. arises from the second cervical spinal nerve (C-2).
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 |  |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 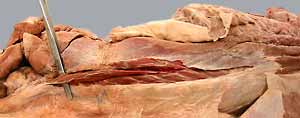 |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 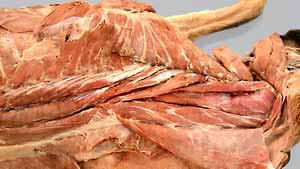 |
 |
6 |
| 7 |  |
 |
8 |
| 9 |  |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 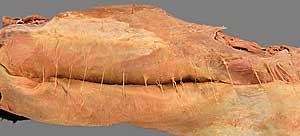 |
 |
12 |
| 13 | 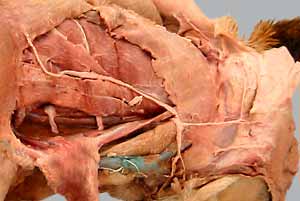 |
 |
14 |