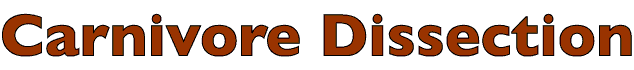
LAB 13 Introduction
Thoracic Limb:
Proximal Vessels and Nerves
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 125-139)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
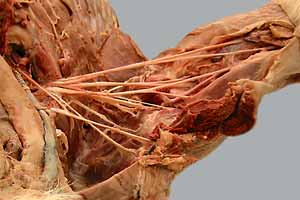
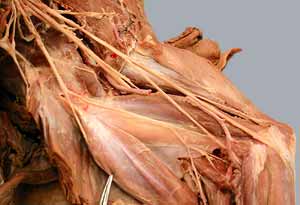
• Identify branches of the subclavian a.:
- vertebral a. (runs through a canal in cervical vertebrae)
- costocervical trunk (supplies first three intercostal aa.)
- internal thoracic a. (seen previously)
- superficial cervical a. (runs toward superficial cervical lymph nodes)
• Identify branches of the axillary a.:
- external thoracic aa. (supply pectoral mm.)
- lateral thoracic a. (runs near the axillary lymph node)
- subscapular a. (gives off the thoracodorsal a. to the latissimus dorsi m.)
- cranial circumflex humeral a. (caudal circumflex humeral a. is from the subscapular a.)
• Identify branches of the brachial a.:
- two cranial branches: bicipital a. & superficial brachial a.
- two caudal branches: deep brachial a. & collateral ulnar a.
- a large artery, deep to pronator teres m.: transverse cubital a.
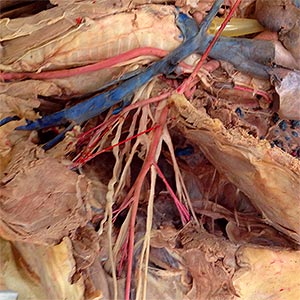
Brachial Plexus
• The following nerves innervate extrinsic muscles of the limb or the cutaneous trunci m:
- thoracodorsal n.: innervates latissimus dorsi m.
- pectoral & cleidobrachialis nn.
- lateral thoracic n.: innervates cutaneous trunci m.
• The following nerves innervate scapular intrinsic muscles:
- suprascapular n.: innervates supraspinatus & infraspinatus mm.
- subscapular n.: innervates subscapularis m.
- axillary n.: innervates teres major & minor & deltoideus mm. (sends branches to subscapularis m.)
• The following nerve innervates elbow flexors:
- musculocutaneous n.: innervates biceps brachii & brachialis mm.
Anatomical Terms:
Thoracic limb: arteries
subclavian a.
superficial cervical artery
axillary artery
external thoracic a.
lateral thoracic a.
subscapular a.
thoracodorsal a.
caudal circumflex humeral a.
cranial circumflex humeral a.
brachial artery
deep brachial a.
bicipital a.
collateral ulnar a.
superficial brachial a.
cranial superficial antebrachial a. (do not need to identify)
Thoracic limb: nerves (scapular & brahium regions)
Brachial Plexus
cranial pectoral nn.
suprascapular n.
subscapular n.
musculocutaneous n.
medial cutaneous antebrachial n. (do not need to identify)
axillary n.
cranial lateral cutaneous brachial n. (do not need to identify)
thoracodorsal n.
radial n.
median n.
ulnar n.
caudal cutaneous antebrachial n. (do not need to identify)
Note:
supra- [Latin] = above & sub- [Latin] = under; suprascapular and
subscapular nerves are name for their positions in humans.
Instructor Commentary:
The brachial plexus innervates the thoracic limb including four extrinsic muscles of the thoracic limb.
The plexus arises from ventral branches of spinal nerves: C-6, C-7, C-8, and T-1 (T-2 may contribute
significantly in some individuals). (At the cranial edge of the brachial plexus, the phrenic n. arises from
C-5, C-6, and C-7 and innervates the diaphragm.)
Nerves from the brachial plexus may be grouped as follows . . .
A] Nerves to extrinsic muscles of the thoracic limb:
- pectoral nn. (cranial to superficial m. and caudal to deep pectoral m.)
- nerve to cleidobrachialis m.
- thoracodorsal n. (to latissimus dorsi m.)
- long thoracic n. (to thoracic part of serratus ventralis m.)
also, lateral thoracic n. to cutaneus trunci m. (not a limb muscle)
B] Nerves that innervate intrinsic muscles of the scapular region:
- suprascapular n. (to supraspinatus and infraspinatus mm.)
- subscapular n. (to subscapularis m.)
- axillary n. (see below)
C] Nerves that run to the lateral surface of the thoracic limb:
- axillary n. (runs laterally, caudal to the shoulder joint). It supplies flexors of the
shouder joint (teres major and minor, deltoideus, and subscapularis mm.).
It supplies skin of the lateral brachium.
- radial n. (runs laterally in the brachium). It supplies extensor muscles of the elbow,
carpus, and digits. It is sensory to the cranial surface of the antebrachium
and the dorsum of the manus (except lateral surface of fifth digit).
D] Nerves that run along the medial surface of the thoracic limb:
- musculocutaneous n., supplies muscles that flex the elbow (biceps brachii
and brachialis mm.) & the coracobrachialis m. It is sensory to the medial
antebrachium (medial cutneous antebrachial n.).
- median n., innervates most of the muscles that flex the carpus & digits (caudal group
of antebrachial muscles). It is sensory to the palmar surface of the manus,
except for the fifth digit.
- ulnar n., joins the median nerve in innervating muscles that flex the carpus & digits
(caudal group of antebrachial muscles). It is sensory to the caudal surface of the
antebrachium and the fifth digit.
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
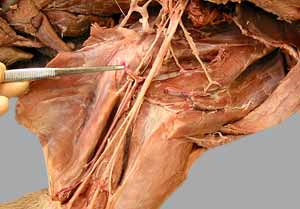
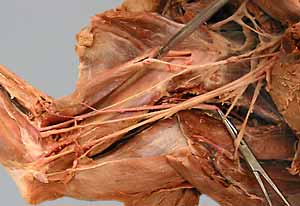
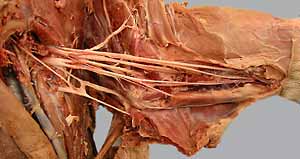
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 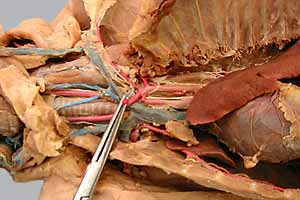 |
 |
2 |
| 3 | 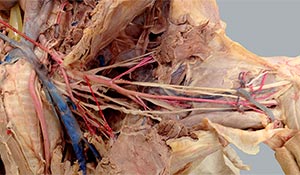 |
 |
4 |
| 5 |  |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 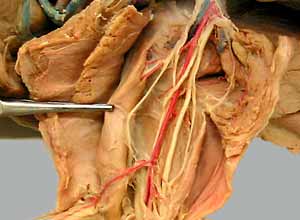 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 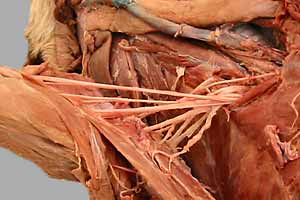 |
 |
10 |
| 11 | 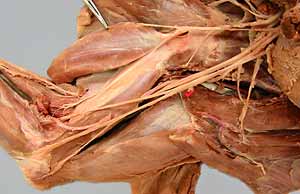 |
 |
12 |