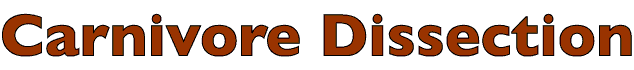
LAB 19 Introduction
Pelvic Vessels and
Pelvic Viscera
(Guide to the Dissection of the Dog, 8th ed., pp. 184-197)
CONTENTS:
Lab Objectives:
• Identify visceral branches of the internal iliac a.:
- umbilical a. (to urinary bladder)
- internal pudendal a. (supplies pelvic viscera)
-- vaginal or prostatic a. (to cranial viscera)
-- caudal rectal a. (to anal canal)
-- artery of penis/clitoris (branches to three erectile bodies)
• Examine pelvic viscera:
- urinary bladder and urethra
- rectum and anal canal
- pelvic genitalia . . .
• Dissect male genitalia:
- prostate and pelvic urethra (cat: bulbourethral glands)
- penis (root, body, free part)
-- three erectile bodies and three muscles
• Dissect female genitalia:
- vulva and clitoris
- vestibule, vagina, and cervix of the uterus
Corrections to Guide to Dissection of the Dog:
• On page 180 (bottom), change "preprostatic and prostatic components" to "preprostatic (cat only) and prostatic components"
• On page 184 (left bottom line), "bulbs of the penis" should be "bulb of the penis"
Anatomical Terms:
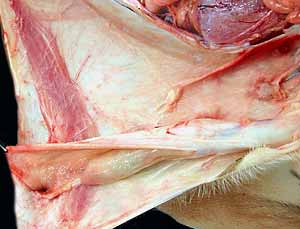
Pelvic vessels
Terminal branches of aorta:
median sacral artery
external iliac artery (enters vascular lacuna)
internal iliac artery
umbilical artery
internal pudendal artery
vaginal a. / prostatic a.
uterine a. / a. of ductus deferens
caudal vesical a.
middle rectal a.
ventral perineal a.
caudal rectal a.
artery of the penis (clitoris)
artery of the bulb of the penis
deep artery of the penis
dorsal artery of the penis
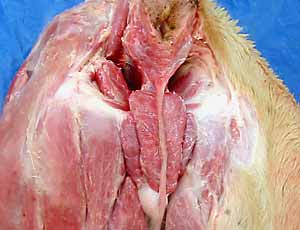
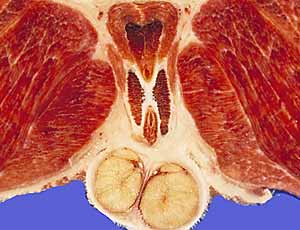
Pelvic Viscera
urinary bladder
trigone of the bladder
median ligament of the bladder
lateral ligaments of the bladder
urethral muscle (urethralis m.)
rectum
anal canal
columnar zone (has anal columns)
anocutaneous line (intermediate zone)
cutaneous zone [palpate]
anal sac (paranal sinus) [palpate opening]
anus
internal anal sphincter m. (smooth m.; not evident grossly)
external anal sphincter m. (striated)
rectococcygeus muscle
Male Genitalia
prostate gland
urethra
pelvic part
pre-prostatic part (cat only)
prostatic part
urethral crest with colliculus seminalis
post-prostatic part -- (covered by urethralis m.)
penile part
prepuce [palpate]
preputial orifice [palpate]
fornix of the prepuce
retractor penis muscle
penis (root, body, & free part) [palpate]
corpus cavernosum penis (paired)
tunica albuginea
crus (at root of penis)
ischiocavernosus m. (covers crus)
corpus spongiosum penis
bulb of the penis [palpate]
bulbospongiosus muscle (covers bulb)
glans
pars bulbus glandis
pars longa glandis
os penis [palpate] (see bone box)
urethral groove
bulbourethral glands (cat)
Female Genitalia
cervix of uterus
cervical canal
internal uterine ostium (uterine body opening)
external uterine ostium (vaginal opening)
vagina
fornix
vestibule
urethral tubercle (dog) groove (cat)
urethral opening
vestibular bulbs (do not need to identyify)
fossa clitoridis [palpate]
clitoris
vulva [palpate]
labia [palpate]
vulval cleft
dorsal & ventral commissures [palpate]
Note:
genitalia is from the Latin: genitalis = pertaining to birth
vulva is from the Latin: vulva = vulva
pudendal -- pertains to external genitalia,
from the Latin: pudere = to be ashamed
Instructor Commentary:
Although the internal iliac artery supplies the pelvis with branches that are named the same in the dog and cat, the branching pattern is different in the two species. Identify branches of the internal iliac artery according to the region being supplied, but learn only the branching pattern seen in the dog:
After giving off the umbilical artery, the canine internal iliac artery divides into a branch that supplies the wall and a branch that supplies pelvic viscera. The visceral branch, internal pudendal artery, sends a branch to cranial viscera (prostatic/vaginal artery) and terminates in caudal viscera (caudal rectal artery and artery to the penis/clitoris). The wall branch, caudal gluteal artery, ends in the rump after giving off two branches that loop around the ilium.
In human anatomy, the term vulva (female external genitalia) includes the vestibule (which is quite compressed in women). In veterinary anatomy, the term vulva is restricted to just the labia because the vestibule is elongate and internal.
Dissection Steps:
Click to view a PDF list of dissection procedures for this lab:
Show List of Dissection Steps (PDF)
Dissection Images:
Note: Click an image to see it enlarged, view its caption, and toggle its labels.
| 1 | 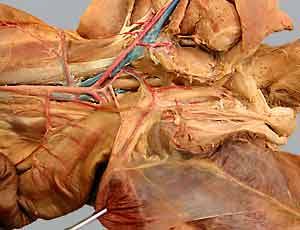 |
 |
2 |
| 3 |  |
 |
4 |
| 5 | 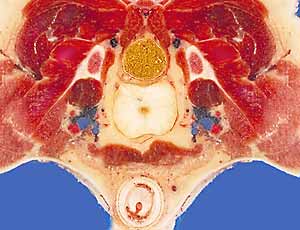 |
 |
6 |
| 7 | 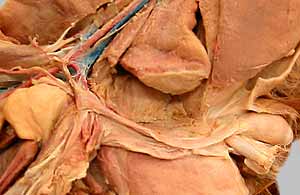 |
 |
8 |
| 9 | 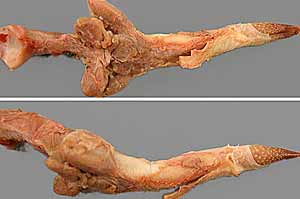 |
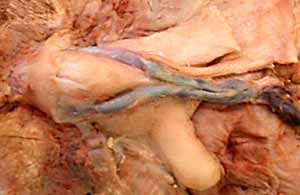 |
10 |
| 11 | 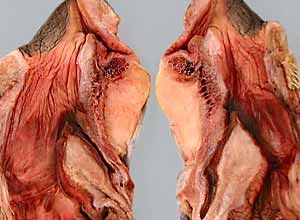 |
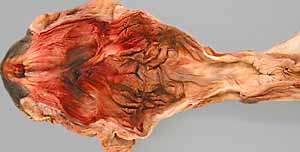 |
12 |