Close
Sympathetic Pathway

Above: Sympathetic peripheral innervation to the bladder & urethra begins with preganglionic neurons located in the intermediolateral nucleus of the lumbar spinal cord (L2-4). The preganglionic axons travel through the ventral root, spinal nerve, and ramus communicans to the sympathetic trunk. The axons continue in lumbar splanchnic nerves to the caudal mesenteric ganglion where the majority synapse. The postganglionic pathway involves a right/left hypogastric nerve and pelvic plexus. Sympathetic postganglionic axons release norepinephrine which leads to contraction of smooth muscle in the bladder neck and urethra but inhibition of the detrusor muscle.
Note: A minority of sympathetic preganglionic axons synapse in pelvic ganglia, rather than the caudal mesenteric ganglion. As another means of producing detrusor relaxation, some sympathetic postganglionic axons synapse in pelvic ganglia and block parasympathetic ganglionic transmission.
Below: The caudal mesenteric ganglion and hypogastric nerves are shown in a feline cadaver dissection.
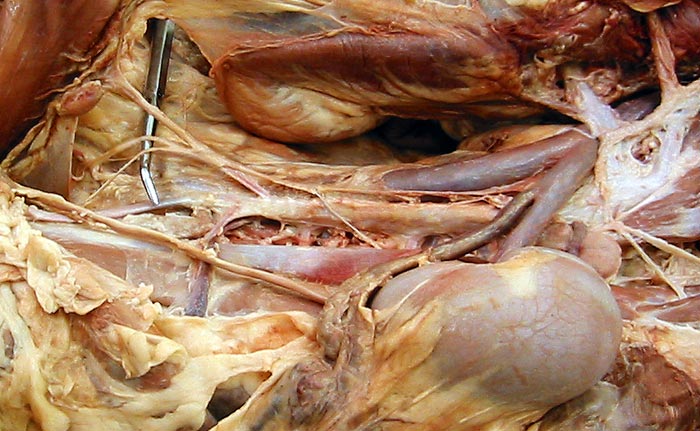

[spacebar toggles labels — esc closes window]
