RETURN
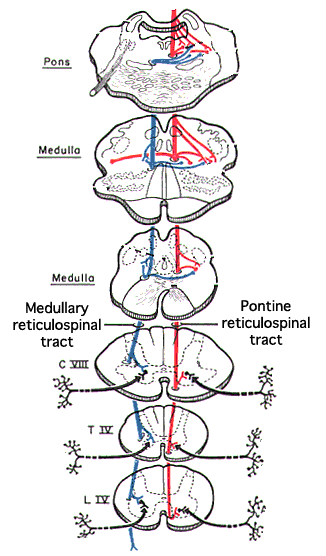
Reticulospinal Tracts
The pontine reticulospinal tract (red) is formed by projection neurons located laterally in the pontine reticular formation.
The pontine projection neurons receive vestibular and non-specific synaptic input which keeps them spontaneously active.
The pontine tract activates gamma and apha motor neurons that innervate extensor muscles. Thus it drives muscle tone.
The medullary reticulospinal tract (blue) originates from projection neurons located medial and caudal to the pontine tract.
The medullary projection neurons are not spontaneously active. They must be activated by specific synaptic input.
The medullary reticulospinal tract inhibits extensor muscle tone and activates flexor muscles.